
Life story work can help care workers and relatives connect with people with dementia
An NIHR-funded feasibility study about life story work with people with dementia showed how the approach could help people connect.
- Published: 11 November 2022

An NIHR-funded feasibility study about life story work with people with dementia showed how the approach could help people connect.

Combining computer-based speech and language therapy with usual NHS care can help some people improve their communication following a stroke.

Researchers from three NIHR Health Protection Research Units have found that flooding can have a significant negative impact on the mental health of people whose homes are flooded, as well as those whose lives are disrupted by flooding events. Their research has informed guidance for local authorities, policy makers and public health practitioners on planning for and dealing with the aftermath of a flood.

Innovative research into the provision of communication aids for non-speaking children has created new guidance to improve the way aid is provided.

A simple technique in which patients hold their breath for up to 20 seconds to spare the heart from radiotherapy during breast cancer treatment has been adopted as the standard of care across many UK hospitals.

Evidence from a gene therapy trial has contributed to a partnership between researchers and commercial companies to develop clinical trials and a potential treatment for cystic fibrosis

Find out how our funded research has influenced policy and helped to prevent 8,000 miscarriages a year.
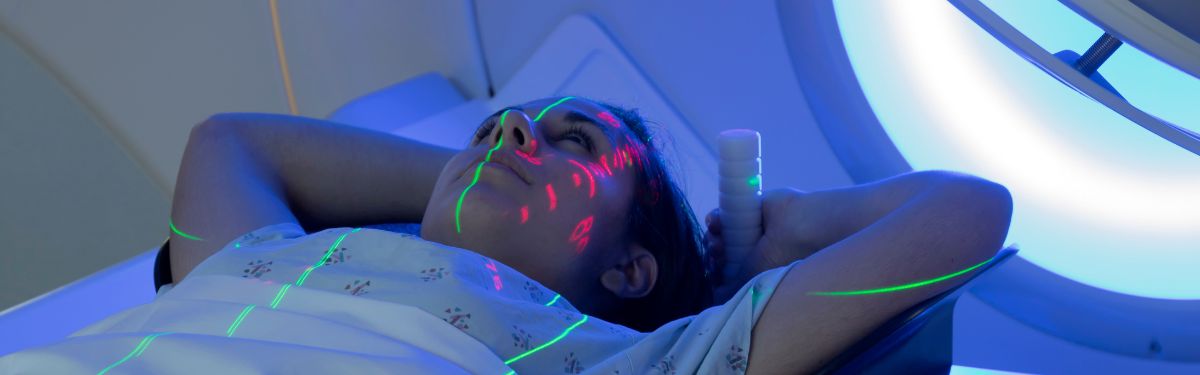
Breast cancer patients in the UK can now receive fewer radiotherapy sessions following surgery after the FAST-Forward trial confirmed that a one-week course was as safe and effective as the standard three-week course. The new treatment schedule is now being adopted internationally.

NIHR researchers have developed new ways of diagnosing and treating severe bleeding after traumatic injury.

The NIHR-funded Optimal study showed how care home and NHS services can work together to improve residents’ care. Its results have informed national policy and shaped changes to service delivery to improve the quality of life, health care and health planning for people living in care homes.

A team at the NIHR Maudsley Biomedical Research Centre has developed a series of new approaches to improve treatment and support for patients with anorexia nervosa and their caregivers at all stages of the illness. Their evidence-based interventions and models of care have been integrated into NICE guidelines and widely adopted within the NHS.

A study of 6 to 7 year-old children carried out by NIHR-funded researchers found that school-based interventions alone are unlikely to improve childhood obesity. The results have informed the NHS and other public agencies about the most appropriate methods to prevent and manage childhood obesity.

NIHR-funded researchers developed a data platform called CALIBER for more than 30 studies on the onset and progression of cardiovascular diseases. CALIBER has now expanded to provide access to linked data on more than 50 million patients and has supported over 100 research projects across a range of conditions, including COVID-19.

A low-cost talking intervention has been shown to prevent tooth decay in children. NHS dental nurses are now offered training in the technique, and commissioners in the North West have committed to introducing the intervention into dental services.

Evidence from NIHR-funded research contributed to a change in immunisation policy that made the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine available to boys as well as girls, potentially preventing more than 100,000 cancers over 50 years.

NIHR researchers used interviews with older people in South Yorkshire to develop a website and other resources to help health and social care providers and organisations support vulnerable older people to keep warm and well during cold weather. Their resources have informed national and local support aimed at improving older people’s living conditions.

NIHR-funded researchers have developed a model called QCovid® that predicts the risk of people becoming seriously ill or dying from COVID-19. The model has been used to inform UK health policy, and its use by NHS Digital helped prioritise 820,000 people for vaccination.

Free bus travel in London is a socially inclusive way for young people to access education, services and social activities without reducing their physical activity levels or displacing other age groups from bus travel.

Interactive digital interventions (IDIs) are effective for sexual health promotion and HIV prevention. They could be rolled out much more widely to complement school sex and relationships education and sexual health services.

NIHR researchers have shown that early cancer diagnosis rates can be improved in primary care by increasing symptom awareness and reducing referral delays. Their research has contributed to national guidance developed to support GPs’ decision making and improve cancer survival rates in the UK.

Researchers investigating the role of IBS-specific CBT have found that both telephone and web-based CBT helped patients to better manage their condition, reducing the severity of their symptoms and the impact of IBS on their lives compared with their usual treatment.

A study identifying key strategies to improve the influenza vaccination rate among people at risk of serious disease has informed guidelines used by general practitioners to plan and deliver their annual vaccination programmes.

The PARTNER2 study has confirmed that antiretroviral treatment for HIV reduces the risk of sexual transmission between gay male partners to zero.

NIHR researchers have shown that a surgical procedure for young children with cerebral palsy improves their mobility and quality of life. The procedure is now available to eligible children on the NHS as a result of this evidence.

The FINCH study has reported new evidence to inform the management of care home residents with dementia who experience faecal incontinence.